Neural quantum states
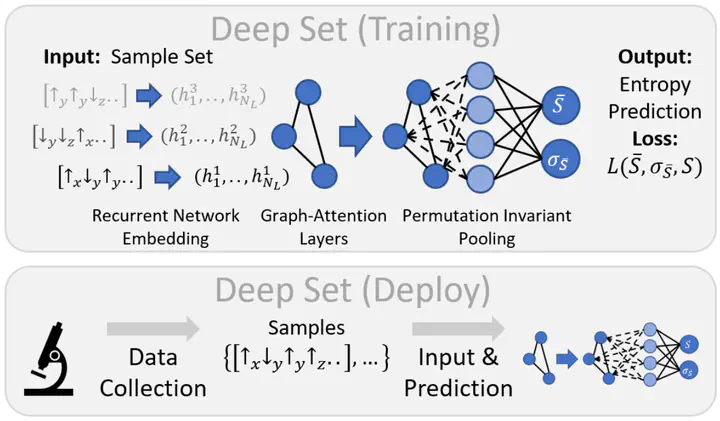
Artificial neural networks have proven extremely successful for machine learning tasks such as computer vision and speech recognition. Specifically, generative models can be trained to approximate probability distributions based on data samples. Quantum states are represented by high-dimensional probability distributions, inviting the use of generative models for finding efficient state representations. We use this approach to develop numerical tools for calculating the time evolution of quantum many-body states and to do quantum state tomography. Furthermore, we use supervised learning to efficiently predict entropic quantities from measured data.
